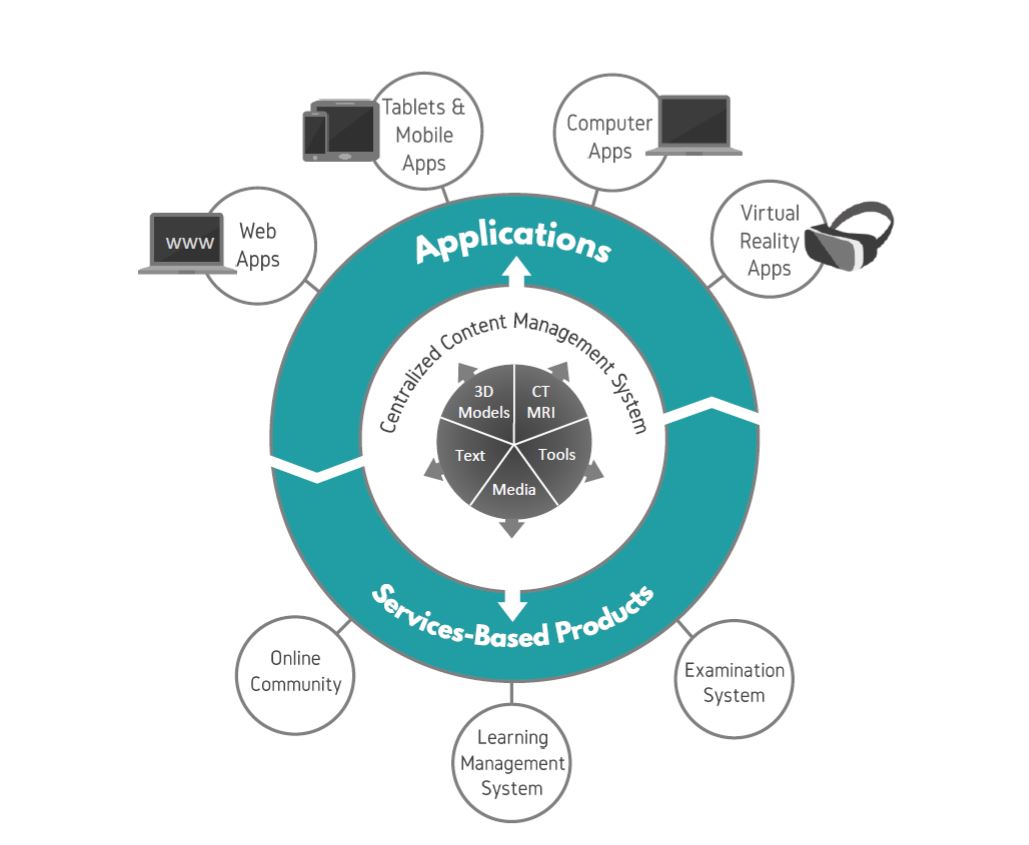
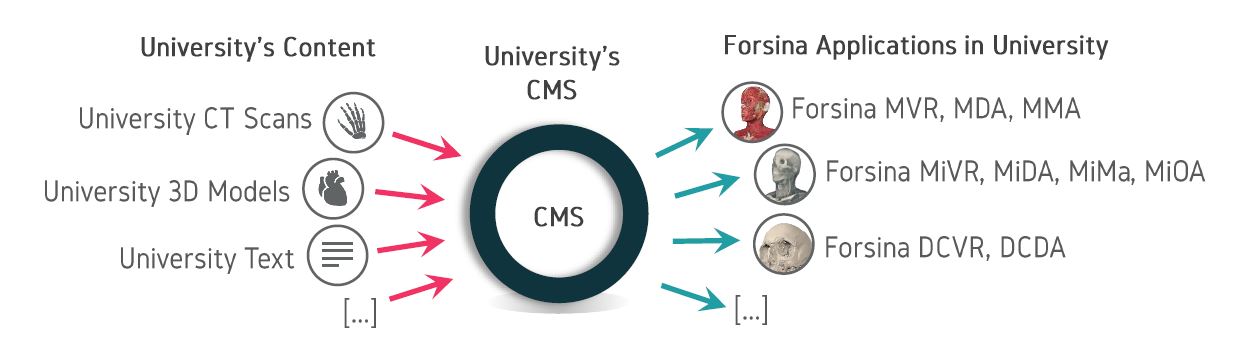
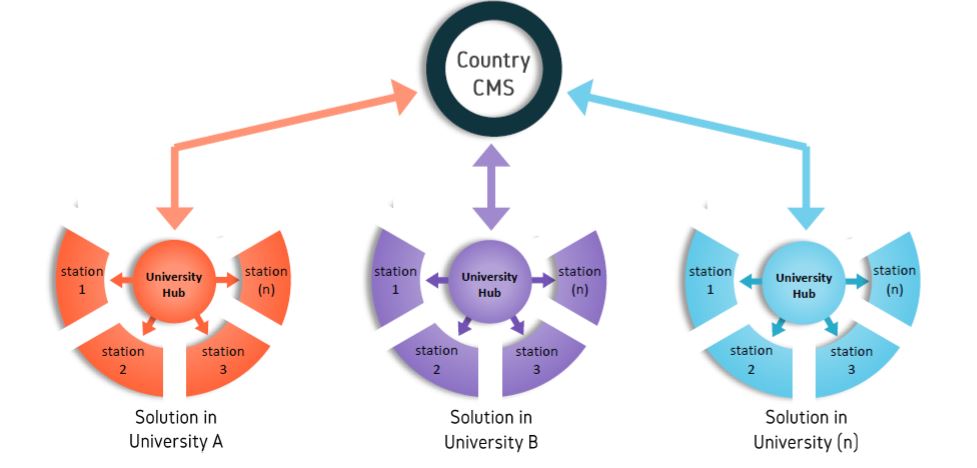
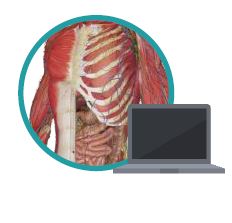
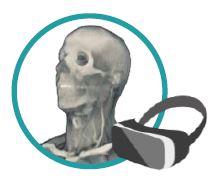
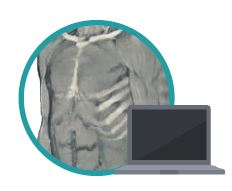
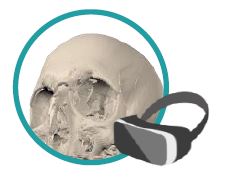
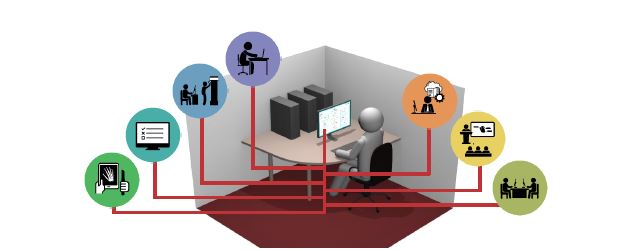
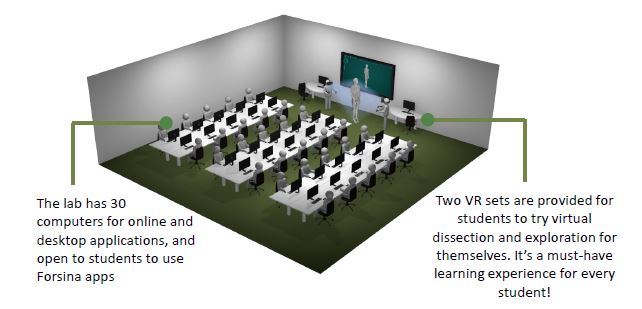
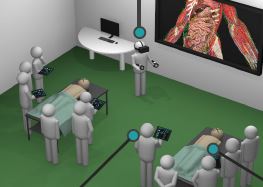
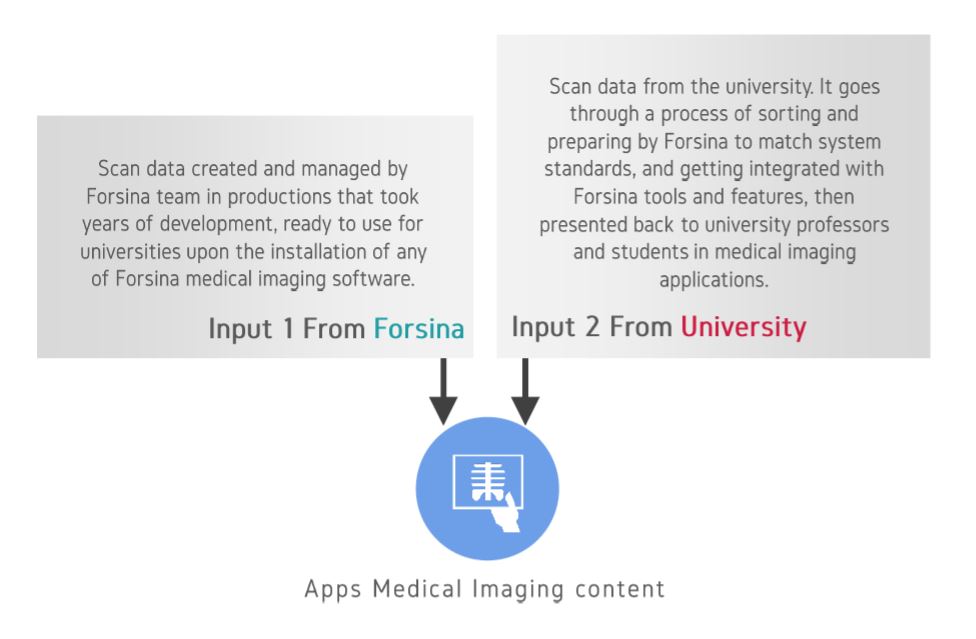
The education process of health sciences in universities is suffering from deficiencies of the traditional teaching methods. Although healthcare is advancing at a fast rate, medical education is still lagging behind. Technology is advancing in a mad rate and has become embedded in every aspect of our lives. Forsina has come to realize that it’s time to use the latest technology to help the education of health-sciences become better and more efficient. Using three-dimensional (3D), computer-generated (CG) graphics will benefit the teaching of complex subjects like human anatomy, in which understanding the shape of objects and spatial relations between parts is necessary. Using Virtual Reality technology to simulate environments digitally and enable users to live inside them, has proved of huge benefits for military and aviation training, and it can be employed to serve the much-needed sector of healthcare, especially for surgical training and patients’ diagnosis. Most educational digital products in the market have limited scope and target students solely. Forsina has created a series of highly-advanced software, in terms of content, performance, and features, to cover the needs of all parties of the education process, with special emphasis on administration and professors’ needs. Forsina gathered all these products in one harmonized complete solution for universities.